Many of our customers don’t start out looking to implement Demand-Driven Manufacturing per se. Often, they’re focused on Lean Manufacturing or at least some element of it. In fact, customers often find out about us as they search for an eKanban or production scheduling solution that will work with their current ERP system.
However, at some point in the conversation, they will inevitably ask, “Is Demand-Driven Manufacturing the same thing as Lean Manufacturing?”
Demand-Driven Manufacturing isn’t synonymous with Lean or other related initiatives such as Theory of Constraints. Instead, it supports and is supported by them. To understand that, let’s look at basic definitions of each of these philosophies, including Demand-Driven Manufacturing, to see how they are related.
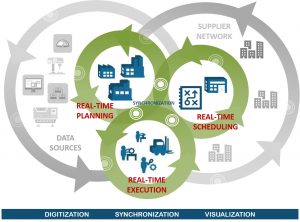
Demand-Driven Manufacturing enables a synchronized, closed loop between customer orders, production scheduling and manufacturing execution.
Demand-Driven Manufacturing is a manufacturing method that enables a synchronized, closed loop between customer orders, production scheduling and manufacturing execution – all while synchronizing the flow of materials and resources across the supply chain.
Another term commonly used for Demand-Driven Manufacturing is pull-based or demand-pull manufacturing. Instead of producing to what you think will happen (forecasts) or to maximize an efficiency metric like asset utilization, the only variable is actual demand, and all production is synchronized to it.
Both Lean Manufacturing and Theory of Constraints emphasize managing variability as part of a continuous improvement effort.
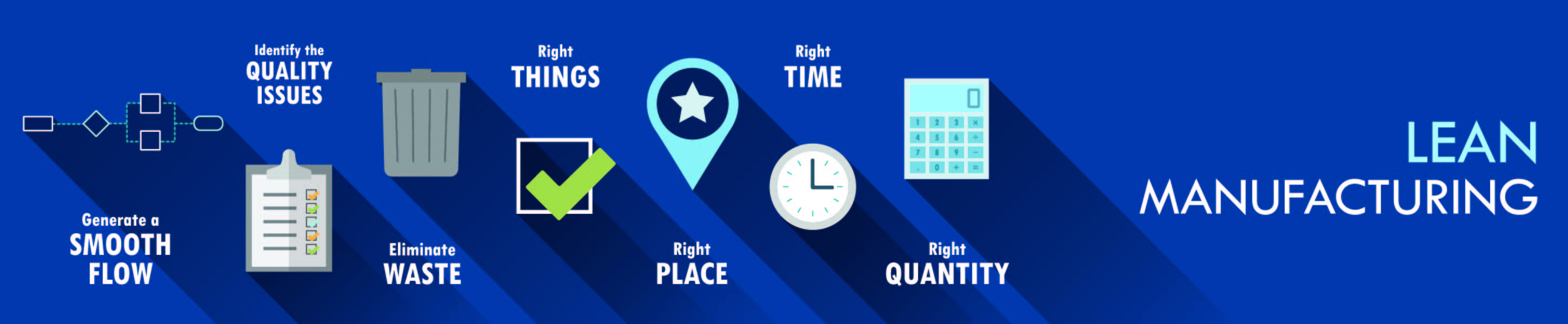
Lean Manufacturing focuses on the removal of waste from the production system; waste being defined as anything the customer isn’t willing to pay for. Pull manufacturing isn’t the same thing as Lean, but it is one of the five principles of Lean as defined by Womack and Jones in their landmark book Lean Thinking. So, at some point in your Lean journey, you should be replacing your push-based production scheduling approach with one that is pull- or demand-based.
On a side note, going from push to pull is almost impossible to do when your schedule is reliant on the push-based logic found in most ERP systems. (Most notably MRP and APS.) That’s why we developed Synchrono software, including SyncManufacturing, as web-based applications that can be easily used with your existing systems. For a more thorough discussion on push vs. pull, download our white paper The Next Generation of Planning and Scheduling Solutions.
Demand-Driven manufacturing is also one of the easiest and quickest elements of Lean Manufacturing to implement. Even though it’s number four on the list of five principles of Lean, you don’t have to get through numbers one through three before you can start realizing benefits such as reduced lead times and lower inventory levels.
Theory of Constraints (TOC) emphasizes increasing throughput. Be careful though. In the vernacular of TOC, throughput does not refer to production. Instead, throughput is the rate at which the organization generates money by producing finished goods that are sold. Excess inventory sitting in the warehouse is not counted. That tightly matches Lean philosophy in that Lean defines waste as anything the customer is not willing to pay for. Excess inventory and the storage and handling of it certainly falls into that category.
A constraint is defined as anything that limits throughput. Inside the facility, that is often a work center. Instead of managing the production capacity of every work center, TOC focuses on synchronizing production to the constraint. This is a vital component of Demand-Driven Manufacturing as well, and you can see how this works in this excerpt from one of our recent webinars.
I hope this discussion not only helped clarify the differences between these common manufacturing philosophies, but also highlighted how Demand-Driven Manufacturing can help you reach your goals regardless of which philosophy drives your organizational thinking. As always, we welcome your comments – and I’d be happy to answer any specific questions you might have. Just submit them below.